
Insulin Hormone: The Master Regulator of Life
Before getting into the functions of insulin hormone, let us understand what is Insulin? Insulin is the hormone that is responsible for allowing the glucose in your blood to get into your cells, giving them the energy to work. The pancreas responds by producing insulin, allowing glucose to enter body cells for the purpose of providing energy. The pancreas secretes a hormone, insulin, that allows glucose to move from the blood to the cells. It is in its role as an endocrine gland that the pancreas produces insulin, along with another hormone called glucagon. Human insulin is used to treat diabetes mellitus type 1 (insulin-dependent) and 2 (non-insulin-dependent).
Importance of Insulin hormone
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in our body. In humans, it is produced by beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin helps regulate glucose (sugar) levels in the bloodstream. Food breaks down carbohydrates into glucose molecules when we eat it. A person’s bloodstream carries glucose to various parts of the body for use as energy. If too much glucose builds up in the bloodstream, the liver produces insulin to help move it out of the system. This is called insulin resistance. Insulin resistance can lead to diabetes.
People with diabetes need to control their insulin levels. There are various types of processes to take insulin. They can do it either by using insulin injections, syringes, or by using insulin pumps. INSUL by AgVa is the new-age technology-based insulin pump for diabetic patients. It is designed to ease the process of providing insulin to diabetes patients.
Insulin Process in the Body
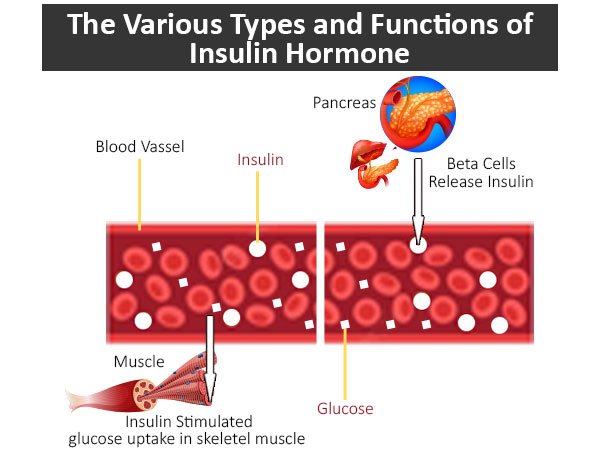
- Clusters of cells called islets in the pancreas make insulin, and they determine how much to make depending on blood glucose levels in the body. Glucose serves as a source of energy because Insulin unlocks cells in the body, allowing for the use of glucose as fuel.
- Raising causes the pancreas to secrete insulin, allowing the glucose to travel within the cells to be used. A rising glucose signal signals to the pancreas to release insulin to remove glucose from the bloodstream. When blood glucose increases, cells in the pancreas secrete insulin, which causes the body to take glucose out of the blood and bring blood glucose back down to normal.
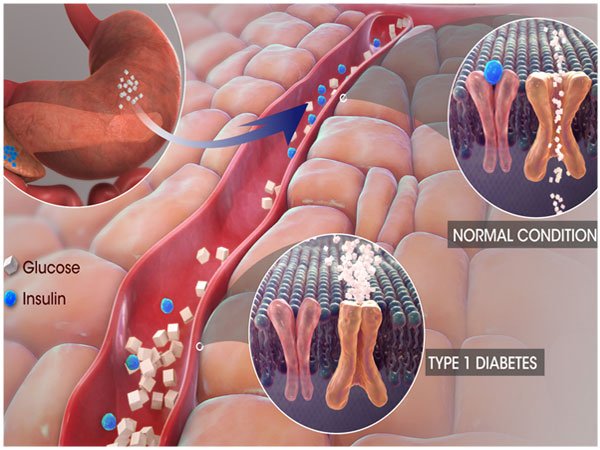
- Higher glucose levels produce more insulin to maintain blood sugar levels. With too little insulin, the body cannot transfer glucose from the blood to cells anymore, which causes higher levels of blood glucose. When blood glucose levels are high, the beta cells in the pancreas quickly produce insulin and release it into the bloodstream, facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for their biochemical energy needs.
- When you eat, your pancreas releases insulin to help your body create energy from glucose, the kind of sugar found in carbohydrates. The hormone insulin works together with glucagon, another important hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas, to make sure that your body is running normal glucose metabolism.
What are the various Insulin problems?
Insulin resistance: The first issue people experience when they have diabetes is high blood sugar levels. This causes damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and other organs. People who have diabetes often feel tired, weak, and thirsty. They may also have blurred vision, dry skin, frequent infections, and an increased risk of heart disease. This can result in high blood sugar levels and diabetes. In some cases, this may lead to obesity, heart disease, and other health issues.
Insulin Overproduction: When you produce too much insulin, you may have type 2 diabetes. When you produce too little insulin, you may have hypoglycemia. Both of these conditions are dangerous and require immediate treatment.
Hypoinsulinemia: Hypoinsulinemia occurs when your pancreas produces less than normal amounts of insulin. This causes your cells to become resistant to insulin and leads to poor glucose control.
The various types and functions of Insulin hormone
There are two types of insulin: Regular insulin and Lispro insulin.
Regular insulin has been used for many years in hospitals and clinics. Regular insulin is a type of insulin that has been purified from human urine. In diabetes mellitus, this insulin forms the basis of treatment.
Lispro insulin on the other hand was developed in the 1980s and is now widely used in diabetic patients. Lispro Insulin is a fast-acting insulin that helps control blood sugar levels before meals. Diabetes patients should use this type of insulin because it works faster than regular insulin.
Now let us look into the various functions of insulin hormone below.
Understanding the functions of Insulin Hormone
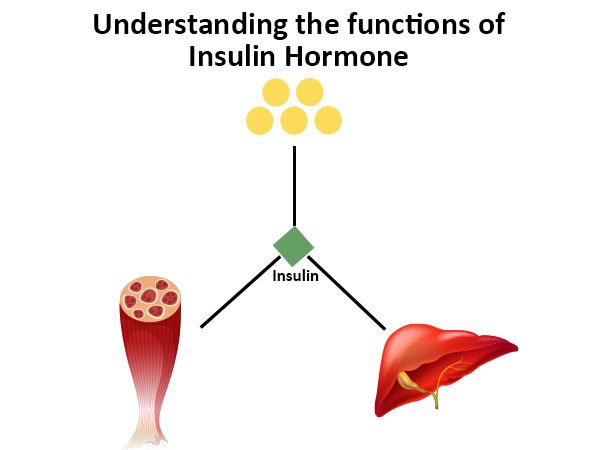
One of the major functions of Insulin hormone is to control blood glucose levels and prevent hyperglycemia. The second most important role of insulin in the human body is that it interacts with glucose, to enable cells of the body to use glucose for energy. Insulin has many functions, but its primary duty is converting the glucose (sugar) in what we eat to a form that the body can use as energy. The primary actions that insulin has been allowing glucose into cells for use as energy, and keeping the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream at a normal level.
Role of Insulin hormone in managing Type 1 Diabetes: A person with type 1 diabetes does not produce enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels normal. Without insulin, glucose stays at elevated levels in your bloodstream.
Role of Insulin hormone in managing Type 2 Diabetes: The pancreas produces insulin at first, but your body’s cells are unable to use the insulin well. People with type 1 diabetes have missing or dysfunctional beta cells, so they lack the hormones insulin and amylin, and GLP-1 cannot function normally.
Are there any other functions of insulin hormone?
Definitely yes, Besides regulating glucose levels, insulin has a number of other functions in the body. Insulin may play a role in:
- Enhancing enzyme activity in the body and resulting reactions.
- The process of repairing muscle damage and enhancing size and strength by transporting amino acids into muscle tissue following sickness or injury.
- Assists in the uptake of amino acids, DNA replication, and protein synthesis.
- By taking lipids into fat cells and converting them into triglycerides, it manages lipid synthesis in the body.
- Maintaining the breakdown of protein and lipids in fat cells as a result of changes in fat cell composition.
- We cant take amino acids and potassium without insulin.
- Maintaining sodium excretion and fluid volume in the urine.
- Making the brain better at learning and remembering.
What will happen without Insulin in our body?
Without insulin, your blood sugar level would rise and fall rapidly. This can lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Hypoglycemia can cause confusion, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, irritability, hunger, sweating, weakness, shakiness, and even seizures. Hyperglycemia can cause blurred vision, dry mouth, fatigue, nausea, palpitations, trembling, and vomiting. It is important to treat either condition as soon as possible since both are dangerous.
The Final Words,
Insulin is a hormone that plays a major role in regulating blood sugar levels. Many functions of insulin hormones in the human body make it an important hormone of the body. The pancreas secretes this hormone to regulate blood sugar levels. The function of insulin is to transport glucose from the liver to the cells. Aside from fat storage, insulin plays a role in protein synthesis as well. There are many functions of the insulin hormone apart from just regulating blood sugar levels.