Notification
Dear Customer,
Thank you for being a valuable member of the AgVa community and for pre ordering the Agva insul pump.
Due to some regulatory problem, there is a delay in lauching insulin pump in India.
We will keep you informed on this shared journey and hope to come back soon with news of starting delivery of pump.
Thank you so much
Date: 21 June 2024
Currently, AgVa Insulin Pump Status
Updated on - 21 June 2024
- The prototype of the Device is prepared, and in-vitro testing mode is complete.
- All consumables have moulds, and the same have undergone test manufacture.
- The EMI/EMC pre-compliance testing has finished.
- Application and documentation for complete CE certification are currently being processed. By the end of the 2024, CE certification is anticipated.
- We have redesigned the battery & charging system. Now, AgVa Insulin Pump will feature a built-in li-ion battery chargeable via an in-built USB port. We expect the battery to last approximately 15 days on a single charge.
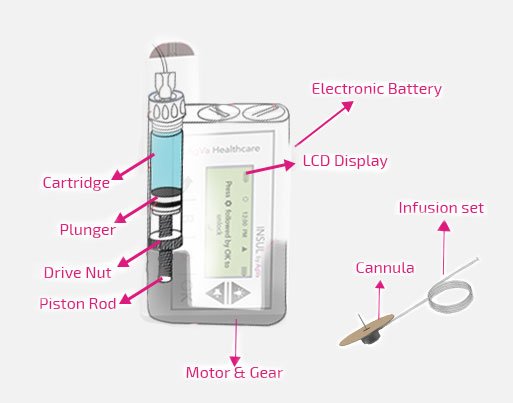
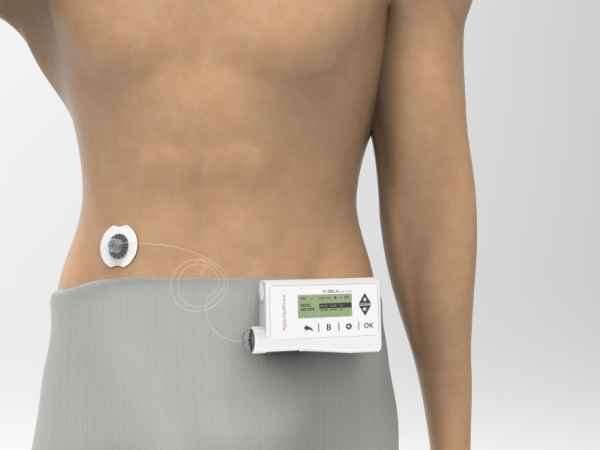
Components of AgVa Insulin Pump
Insulin Pump

Cartridge

Insulin Pump with Cannula

Disposable Sets
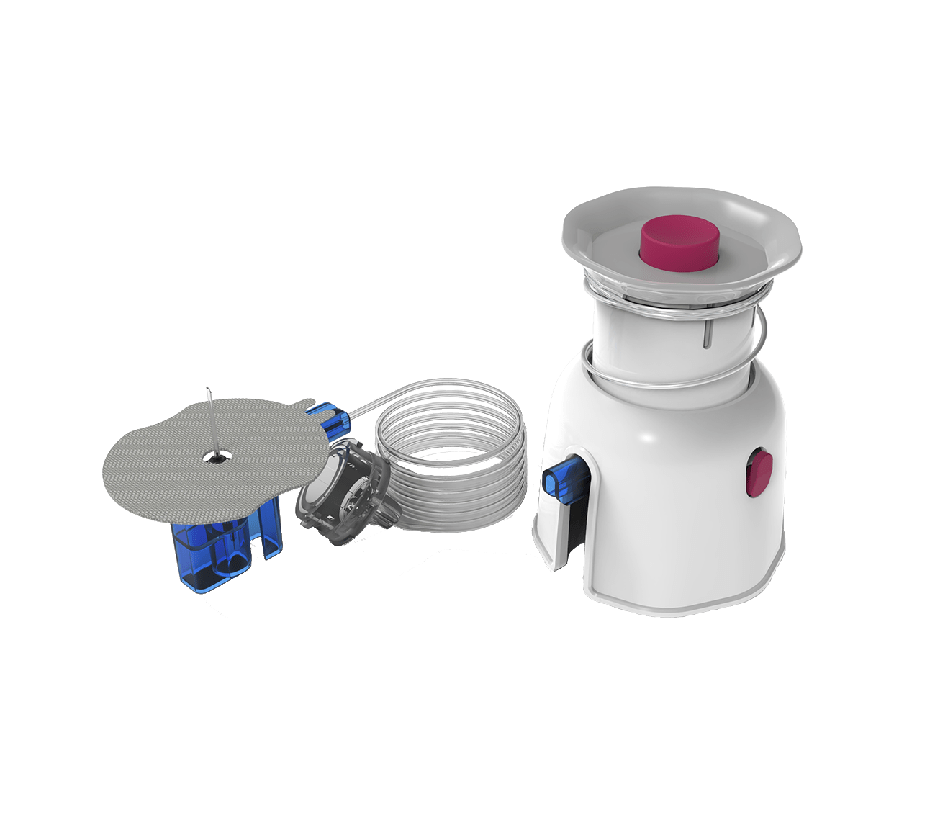
These are the main elements: Insulin Pump, Cartridge, and Disposable Sets.
Roadmap of AgVa's Insulin Pump
An overview of all important phases of INSUL by AgVa development.

Research & Development
PCB Development process
The development process of the AgVa Insulin Pump started in mid-2020 with careful research and material testing. A 6 layer PCB design is used for the insulin pump’s high density components.
PCBs with six layers are ideal for infusion pumps because they generate less EMI interference than four layers or two layers and are more thermally efficient.
AgVa Engineers began their component-sourcing process by contacting potential suppliers. The engineers carefully reviewed all of the potential suppliers’ datasheets to select those components that would best meet the technical requirements and offer the highest value.
Our team then ran thorough tests on each part in the inbuilt clean room to check for functionality across different environmental conditions. We also simulate usage conditions, mechanical stability tests and more.
Specification
Disposable Attachments

Assembling disposable components for insulin pumps involves a combination of automated and manual processes. The first step is to shape basics like tubing connections, adhesives, labeling, and infusion lances using specialized injection molding tools.
After automated cleaning cycles, parts are sent to assembly to ensure they are clean and free of contaminants. After creating disposables for an insulin pump, the final step involves assembling them into sets that will be installed inside the pump reservoirs.
We understand that the LCD screen of an insulin pump is critical in ensuring its safety and performance, and the way the LCD display is formatted plays a critical role in the user-friendliness of the product.
The LCD display has a light green background for easy readability and has multiple icons including that “battery health” “Bolus” and “Basal Dosing” so that all important functions are visible at a glance.
Also, all errors are shown prominently on the screen with a marking icon as well as an audible alarm.
LCD Display

Brushed DC Motor
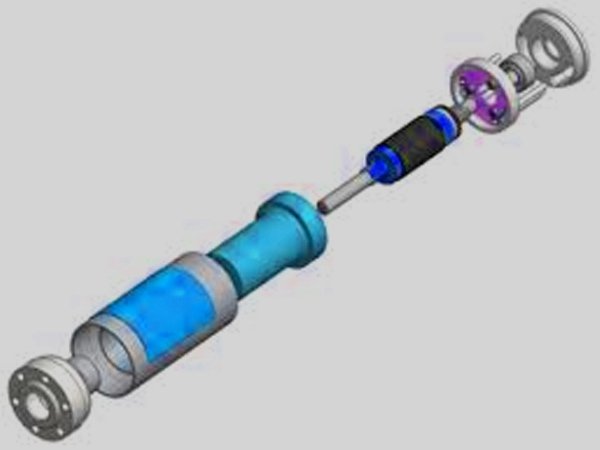
Initially, we needed to understand what kind of motor gearbox would best serve our needs. In a medical product such as an insulin pump which needs to reliably operate over a long period of time without needing too much maintenance or repair, efficiency was extremely important.
We looked at several different kinds of gearboxes before reaching a final decision. We then conducted tests on several prototypes before deciding which one provided us with the highest efficiency ratio and accuracy for powering our insulin pump.
During this testing phase, it became clear that using a brushed DC motor with reduction gears inside it was the way forward to get maximum efficiency from the system while still being cost effective. Additionally, by using reduction gears inside the motor, more torque can be obtained without needing extra components such as separate motor drivers and power supplies thus reducing complexity and cost.
When we were designing our insulin pump, we made sure that pump electronics must be encased in a sturdy, reliable material that protects them from moisture and jolts.
A variety of materials was used for this process, including plastic, metal, and rubber. Each material provides unique aesthetic and performance benefits based on the type of design.
Casing
Pre-loaded Customized Software

The first step in creating an insulin pump with embedded software was to design the system architecture. This included identifying various components like sensors, actuators and microcontrollers, as well as defining the data communication protocols between them.
We had to consider different aspects such as cost-effectiveness, compatibility with existing hardware and software solutions, scalability and robustness of code.
We conducted In Vitro testing for our insulin pump over the course of three months on various types of tissue samples from an animal model. During this time, the AgVa insulin pump was subjected to various stress tests including vibration, temperature change, and shock.
It was tested for accuracy of timing, communication latency time (the interval between signal transmission), signal integrity (signal strength measured by amplitude modulation/demodulation of AM/PM) migration along different surfaces, torque stiffness in both directions (opening/closing handles), as well as sealability test (leakage test).
The In Vitro testing results were positive with respect to all parameters evaluated where the insulin injection accuracy rate was satisfactory beyond 95%. All in all, we are satisfied with our initial results obtained through.
Prototype under Testing

EMI / EMC Testing
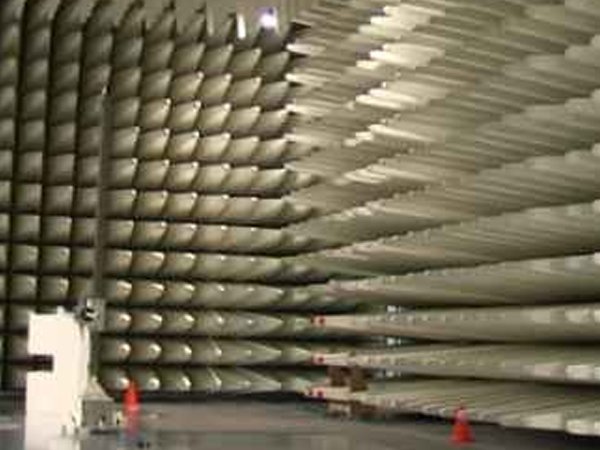

At our R&D facility, we performed EM Tests in accordance with relevant standards. We have taken several steps in order to ensure that no electromagnetic waves or energy emitted by the device will interfere with other electronics or safety systems, and that none of the electrical devices surrounding it will cause a malfunction in the device.This ensures our products exceed safety regulations set out by both domestic & international organizations related to medical electronics design & manufacture.
We have taken several steps to implement comprehensive EMI/EMC tests on our insulin pump prior to releasing it into consumer hands so that users can have confidence knowing their device is both safe and compliant with existing laws pertaining to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and compatibility (EMC).
It’s been a long, hard road from concept to completion. After months of careful planning and time-consuming development, our team finally finished the Technical Manual & User Guide for our insulin pump.
Creating an effective technical manual is key to helping users understand the product’s features, use cases, safety guidelines, and more. To create ours, we followed a number of steps to ensure the technical content was accurate and complete while user experience remained immersive and enjoyable.
First, we gathered feedback from industry experts and users alike on what they wanted out of the user guide. Next came the development stage where we took the information from earlier stages to draft a comprehensive product guide from scratch. Finally, document validation was carried out before finalizing the document by extensively double checking all aspects mentioned earlier along with developers validating software information necessary for optimal functioning.
Manual User Guide

Research and Development Team and Facility



Preorder Now @ ₹499/-
The discount rate is only ₹24,499 rupees for the first 500 customers. Preorders only need ₹499; the remaining payment must be paid when the package is delivered.