Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. DKA is the other name for Diabetic ketoacidosis. When the body produces too many ketones, it becomes acidic and can cause the blood to become thick and foamy. The acetone in the blood can make the blood thick and sticky. This medical emergency can cause death if you don’t do it on time.
Quick fact: It’s the leading cause of death for people with diabetes. However, proper treatment can save lives.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?

First let us understand, what is diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s essentially a type of diabetic coma. It develops when the body’s blood sugar levels become too low. This causes the body to break down fat into ketones. These then enter the bloodstream and cause the body to shut down. This is known as diabetic ketoacidosis. It can cause people to fall into a coma and die. It’s a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Diabetic ketoacidosis can result from either diabetes type 1 or type 2. In both types of diabetes, the body creates too much sugar. However, in type 1 diabetes, the body destroys sugar. In type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t produce enough insulin to regulate sugar. This then causes the sugar to enter the bloodstream and cause the body to shut down. As you can see, diabetic ketoacidosis has many complications. It’s a serious medical emergency.
What are the signs and symptoms of DKA?

The patient will have fruity-smelling breath and urine. Other signs include a fast heart rate, increased heart rate, blood pressure, and low blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis may include:
- Fainting after exercise
- Confusion
- Increased thirst
- Weight loss
- Urine output
- Weakness
- Headaches
- Fatigue
How to Diagnose if you have Diabetic Ketoacidosis?

Diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis requires a combination of signs and laboratory tests. Treatment is immediate and requires a health professional. Doctors will also test their blood sugar levels several times daily to make sure they’re within a safe range. To diagnose diabetic ketoacidosis, a doctor will ask patients about their symptoms and perform a physical exam. They’ll also ask about their eating and exercise habits, and perform a blood glucose test. A blood test will tell if there’s an elevated level of ketones in the blood.
The patient will also undergo several other tests, such as a complete blood count, liver and kidney function tests, and a blood urea nitrogen value. These tests will confirm the diagnosis and help determine the best treatment. The DKA treatment will depend on the patient’s symptoms and blood sugar levels. Patients will be given fluids to prevent dehydration. They’ll be given intravenous fluids to replace lost salts and glucose. The patient will be closely monitored while they’re in the hospital. They should be closely monitored for several days post-treatment.
What are the causes and risks of DKA?
The causes and risks of diabetic ketoacidosis are complex. However, the primary cause of this is uncontrolled diabetes. When the body cannot produce insulin, the body relies on excess sugar for energy. A person with DKA will produce a high amount of acetone in the body. This makes breathing difficult, and the person with diabetic ketoacidosis may lose consciousness. They may also develop a fruity-smelling breath. This is a sign that the body is producing ketones in its bloodstream.
A person with diabetic ketoacidosis will also produce a low amount of glucose in the body. This is because the body cannot produce insulin and is therefore reliant on sugar for energy. The glucose in the blood will be toxic to the body. It can cause cell death and organ failure if left untreated. Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis will exhibit symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. They will also have fruity-smelling breath.
The increase in ketones will cause the body to lose consciousness. This is when the patient will stop breathing and enter into a coma. They will stop breathing due to their body’s inability to produce enough acetone. The person with diabetic ketoacidosis will stop breathing and enter into a coma if untreated. Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis should seek immediate medical attention.
What are the various treatments for DKA?
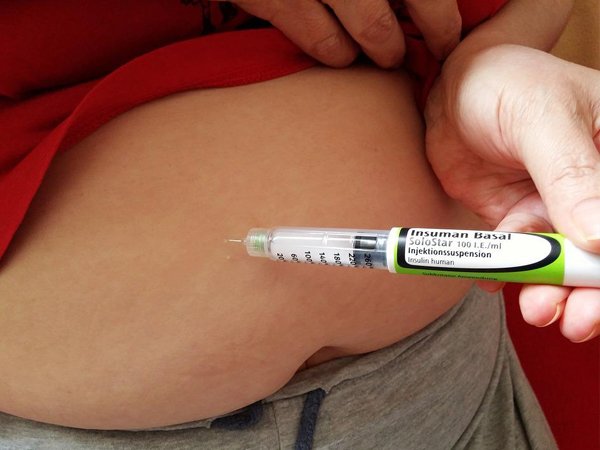
Once you are diagnosed with DKA, you must receive treatment to prevent the complication from worsening. It is treated with insulin. Patients also should eat a healthy diet. Doing so can prevent hyperglycemia, the other name for diabetic ketoacidosis. Preventative measures for diabetic ketoacidosis are very important. The first step in treating this condition is to monitor blood sugar levels. The blood sugar levels must be monitored at all times, even when the patient is feeling well. Patients with diabetes should also choose foods that cause a slow rise in blood sugar levels. They should also eat small meals throughout the day to avoid their blood sugar levels rising too much.
Patients who have DKA must receive insulin therapy to prevent the complication from worsening. There are many ways to take insulin but the easiest is insulin pump therapy. It is a super easy therapy and has a variety of insulin pumps available on the market. A list of some insulin pumps are INSUL by AgVa, Medtronic MiniMed 630G System, Medtronic MiniMed 770G System, Omnipod Dash, t: slim X2, and more.
Patients with DKA can be treated with intravenous fluids (IV) and medications. A close eye must be kept on them until their blood glucose levels return to normal in the hospital. Doctors will closely monitor diabetic patients who have DKA. They will measure the patient’s blood sugar levels and regularly check their blood pressure. IV fluids are administered intravenously. The purpose of these fluids is to replace fluid lost due to diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, and dehydration.
One of the treatments involves the replacement of electrolytes. Electrolytes in your blood carry a charge, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. Your blood electrolyte levels can be lower in the absence of insulin. Your heart, muscles, and nerve cells will function normally when you receive electrolytes through your vein.
Quick Fact: According to a WHO Report, India has about 60 million people suffering from diabetes. By 2025, the number of diabetic ketoacidosis cases in India may reach 1.8 million.
What complications can one have in DKA?

Complications in diabetic ketoacidosis can occur due to the accumulation of ketone bodies in the body. When ketone levels rise, acetoacetate levels rise and can produce acidosis. This occurs when the kidneys are unable to effectively remove ketone bodies from the blood. As a result, the blood becomes acidic and can damage the organs in the body. To prevent this, one must control the blood sugar levels and the kidneys must be able to remove excess ketone bodies.
Over time, however, the blood sugar levels rise, and eating causes a rise in blood sugar levels. As a result, eating causes an increase in blood sugar levels and can again produce diabetic ketoacidosis. For this reason, a person with diabetes must follow a strict diet. The diet must be low in carbohydrates and high in complex carbohydrates.
When to Contact a Medical Professional for DKA?
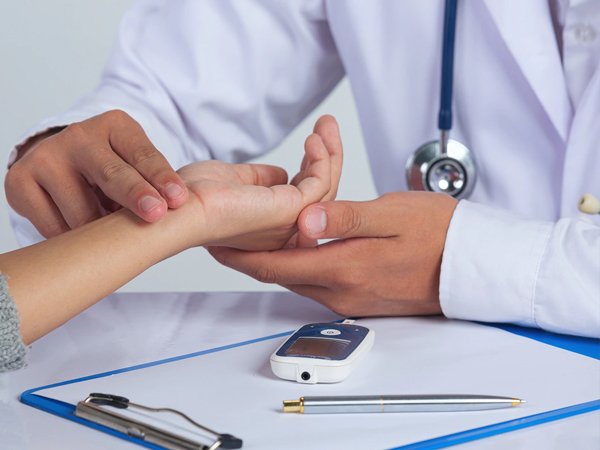
To prevent this serious complication, it’s important to contact a medical professional as soon as you suspect that you have it. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious health condition requiring immediate medical treatment. Hospitalization is possible if the patient continues to experience diabetic ketoacidosis symptoms. It’s important to contact a medical professional as soon as you suspect that you have DKA. Doing so will ensure a safe and controlled environment for the patient. Additionally, the medical professional can use various tests to determine if diabetic ketoacidosis is present. A medical professional should also monitor diabetic ketoacidosis patients to prevent complications.
What You Should Know About Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetic?
It is crucial to treat diabetic ketoacidosis immediately to avoid potentially disastrous effects on the body. The treatment used for diabetic ketoacidosis is the same as that for diabetic acidosis. Both conditions involve the buildup of ketone bodies in the body. However, the treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis focuses on restoring blood sugar levels. First, doctors may use intravenous fluids to hydrate the diabetic patient. Patients with dehydration may also receive intravenous glucose. Doctors may also use insulin to treat the patient’s blood sugar levels. After stabilizing the patient’s blood sugar levels, they can treat diabetic ketoacidosis. Thank you for reading this article. We hope it was helpful to you in several ways. However, you should do your research and consult a doctor before you start anything new. Analyze the factors that affect your blood sugar levels and understand how diabetes affects you in-depth.