Hypoglycemia (lows)
Overview
Hypoglycemia refers to the low levels of blood sugar that may result due to the dropping of blood glucose levels below the normal range. A blood sugar level below 70mg/DL is considered as hypoglycemia and needs immediate treatment. Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar is the most common condition in diabetic people. Taking anti-diabetic medicines, skipping meals and exercising more than necessary may lead to low blood sugar levels.
How does blood sugar works?

Blood sugar is also called blood glucose (BG). The food we eat provides us with a sufficient amount of glucose and brings energy for various bodily functions. Carbohydrates are the main source of food such as rice, bread, potatoes, cereal, fruit, vegetables and milk.
Glucose is absorbed after eating into the bloodstream and travels to other body’s cells. Insulin hormone produced from the pancreas helps in absorbing the glucose in the blood. The body cells then use glucose for energy. If the person eats more glucose than needed, the body will store the extra glucose in the liver or muscles and change it into fat, so that it can be used later in life.
If the body cells don’t get enough glucose, the body stays unable to perform various functions. People who aren’t on diabetic medications have enough glucose to maintain sugar levels. Also, the liver can release glucose if needed. Hypoglycemia can also be a side effect of anti-diabetic medicines.
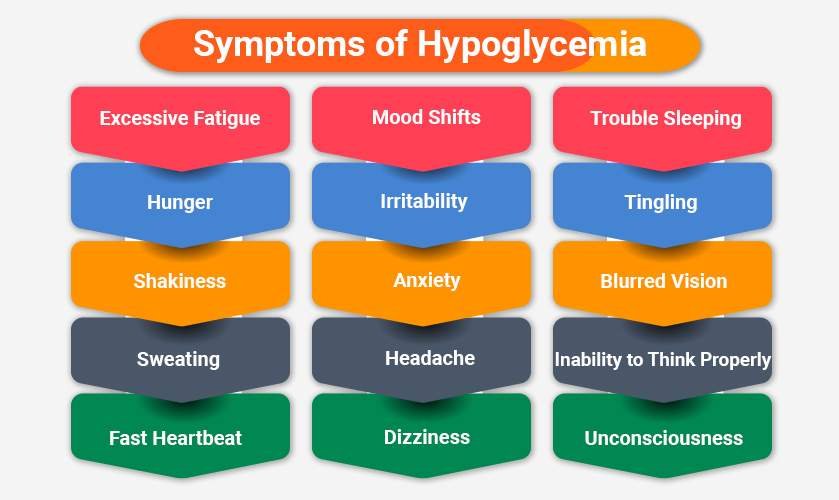
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Excessive fatigue
- Hunger
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Fast heartbeat
- Mood shifts
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Trouble sleeping
- Tingling
- Blurred vision
- Inability to think properly
- Unconsciousness
People with low blood sugar might not know that their BG levels are down and can experience faintness, seizure or can even go to coma.
Causes of hypoglycemia

Insulin is like a key in unlocking the body’s cells to take up glucose. If somebody has diabetes, various treatments can help the cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream. Insulin injections and oral medicines help in elevating insulin levels in the blood. Increased insulin levels with concomitant decrease in BG levels are the most common cause of hypoglycemia
There are a few causes of hypoglycemia in diabetic people:
- Insulin injections or other anti-diabetic medicines
- Skipping meals
- Eating less than usual
- Excessive physical activity
- Drinking alcohol
Causes of hypoglycemia without diabetes:
- Hepatitis
- Kidney disorders
- Tumour
- Adrenal gland deficiency
Diagnosis of hypoglycemia
If the person is non-diabetic and still observes low blood sugars often, then doctors use three methods, known as Whipple’s triad to detect low blood sugar levels.
Signs of low blood sugar levels: the doctor may advise the person to fast or to avoid eating or drinking anything for a few hours, so their low blood sugar levels can be spotted.
Blood test: the person’s blood is taken to test for low blood sugar levels in the laboratory.
The disappearance of signs of hypoglycemia: the doctor will find whether the low blood sugar symptoms disappear when the blood sugar levels are raised.
Treatment of hypoglycemia

When blood sugar is below normal, eating carbohydrates is a must. A diabetic person should keep some sweet thing near to them. According to the American diabetes association, snacks have at least 15g of carbohydrates.
There are a few examples of carbohydrates:
- Sugar candies
- Honey
- Table sugar
- Fresh fruits
- Juice or non-diet soda
- Glucose tablets
Prevention

Prevention from low blood sugar levels will save people from unwanted symptoms and severe complications of hypoglycemia.
There are a few tips to prevent hypoglycemia:
- Diabetic people should monitor their BG levels timely.
- Do not skip meals
- Eat something before a workout
- Keep something sweet to eat