Hyperglycemia (Highs)
What is hyperglycemia?
High blood sugar levels are called hyperglycemia. People with hyperglycemia either don’t produce enough insulin or the body cells are unable to utilise it leading to high blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia. Early diagnosis, avoiding high blood sugar levels and treating the condition soon is essential to treat hyperglycemia at its early stage. Otherwise, hyperglycemia can cause severe complications if left untreated. For a diabetic person, a BG (Blood Glucose) level higher than 180 mg/DL is considered high. High BG levels are common after meals, but if they stay persistent, it can be dangerous.

These are the levels of BG from low to high:
Low BG levels: below 70mg/DL
Normal levels: 70mg/DL-180mg/DL
High levels: above 180mg/DL
Causes of hyperglycemia

Glucose levels can rise due to many reasons such as:
Food: eating food rich in sugars can raise BG levels if the body doesn’t produce enough insulin.
Any illness or infection: some common viral infections such as cold, flu, or stomach virus may cause BG levels to rise more than normal.
Stress: Any kind of stress either physical or emotional may cause high BG levels.
Medications: some medicines either prescribed or over the counter can affect BG levels. If someone observes a shift in BG levels after taking medicines, they should consult their doctor.
Weak Insulin: insulin may lose its strength in extreme heat or cold, or if it has expired leading to high BG levels.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia

Hyperglycemia occurs when BG levels are above normal and it starts showing symptoms within some days, or weeks.
The symptoms of hyperglycemia are:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Headache
High blood sugar
Blurred vision
High sugar levels in urine
Fatigue and weakness
Treatment of hyperglycemia
Insulin is the best option for treating hyperglycemia and lowering excess blood sugar levels. Similarly, some lifestyle modifications can also bring big changes in the BG levels and may treat your high blood sugar. Regular exercise and making necessary changes in diet might bring noticeable results. If the blood sugar level goes beyond 240mg/DL, people should check their urine for ketone, because exercising with a high ketone level may further increase the blood sugar levels.
The doctor may make changes in the medicines or in insulin as a treatment of hyperglycemia.
Complications in hyperglycemia
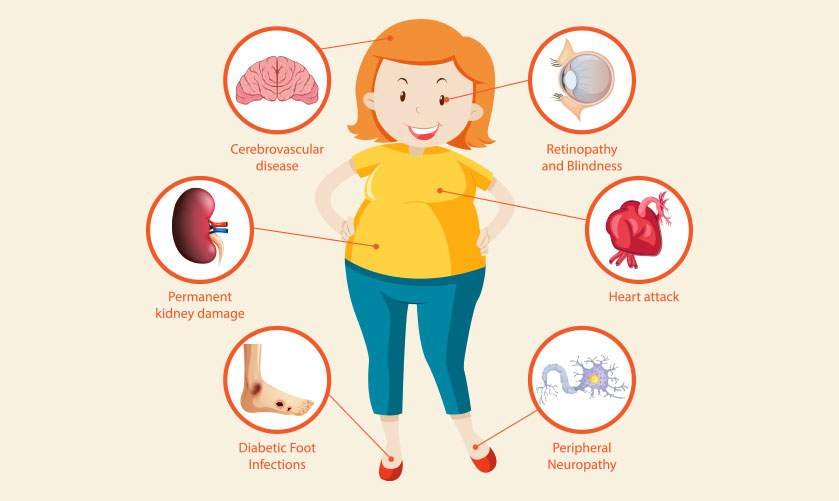
When left untreated, hyperglycemia can cause serious health complications and health risks such as ketoacidosis. In DKA, ketone forms in uncontrollable amounts and the body is unable to release it effectively, leading to ketoacidosis. The person should immediately seek medical assistance if the ketone levels rise uncontrollably.
The person should immediately seek medical help in these conditions:
Nausea and vomiting, Abdominal cramps, Fatigue, Weakness, Dry skin, Hot flushes, Deep breathing and shortness of breath, Fruity breaths, Unconsciousness.
Prevention tips for hyperglycemia

The big prevention tip is to keep BG levels in a healthy range. Good compliance with diabetic medicine and monitoring BG levels timely is crucial to prevent hyperglycemia.
Moreover, a healthy diet and timely meals can prevent hyperglycemia, especially if you are on medicines or insulin. Regular exercise can also lower blood sugar levels. The patient should contact their doctor during any health issue.