
Metabolic Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Metabolic Syndrome (MS) is a condition where your body does not properly metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and sugars. This leads to insulin resistance and increases blood sugar levels. Your body produces too much insulin when you have insulin resistance. This then causes your pancreas to release even more insulin into your bloodstream. Over time this cycle becomes self-perpetuating and results in diabetes. It is a cluster of conditions that increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
One of the main causes of metabolic syndrome is obesity. But it can occur in those who are overweight or obese without being diabetic.
Metabolic syndrome symptoms: what are they?
Abdominal obesity: Abdominal fat is the most dangerous type of fat because it increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer. This is because abdominal fat releases hormones that increase blood pressure and cholesterol levels. People with excess abdominal fat tend to have higher triglyceride levels and lower HDL levels.
High blood sugar: High blood sugar is caused by insulin resistance. Insulin resistance leads to hyperinsulinemia, which causes high blood glucose levels. Hyperglycemia may lead to an increase in inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction.
Low HDL: Cardiovascular diseases are the ultimate cause of Low HDL. A study suggests that people with low HDL had a 2.7 times greater chance of developing coronary artery disease than those with normal HDL.
Elevated blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure causes many chronic conditions including kidney failure, heart attack, and stroke. Hypertension often causes a high level of LDL and triglycerides.
The diagnosis of metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is diagnosed based on the following factors which are:
- Abdominal obesity – A waist measurement greater than 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women.
- Increased fasting blood sugar level – Between 100 and 125 mg/dl (5.6 and 6.9 mmol/L).
- Elevated triglyceride level – 150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L).
- Blood pressure – 130 systolic or 85 diastolic or higher.
What is the best way to manage metabolic syndrome?

You can manage your diabetes by various lifestyle modifications including dietary changes, weight loss, exercise, stress management, smoking cessation, and treatment of comorbidities. Pharmacological therapy includes metformin, thiazolidinediones, statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers. Below are the basic methods to treat this syndrome:
- Exercise: Exercise is the best way to lose weight and improve health. Regular exercise helps burn calories, reduces stress, strengthens muscles, increases energy levels, and improves sleep quality. Exercise also boosts self-esteem and confidence.
- Diet: Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. A balanced diet should contain plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, low-fat dairy products, and nuts and seeds. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
- Stress Management: Stress management is the ability to cope with stressful situations effectively. Stress affects our physical and mental well-being. Managing stress can help us stay calm and focused under pressure.
- Sleep: Sleep is essential to good health. Getting enough sleep at night helps reduce fatigue, boost immunity, and improve mood.
- Medication: Medications may be necessary to treat certain medical conditions. They can also be used to control blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure.
If you have metabolic syndrome, when should you see a doctor?
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of factors that contribute to weight gain and obesity. It is associated with an increased risk for type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, chronic pain, and depression. It is estimated that approximately 25% of adults have this condition.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, then please visit your physician immediately. Below are some of the common symptoms of metabolic syndrome:
- Elevated blood pressure – Blood pressure should always be measured after resting quietly for 10 minutes. Ask your healthcare provider what they recommend measuring your blood pressure.
- Abnormal glucose level – Blood sugar is usually checked after fasting overnight, but it may also be checked before meals.
- Excess body fat – Body mass index (BMI) is often used as a measure of body size. A healthy BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9.
- Abdominal obesity – Waist circumference is another indicator of excess body fat. Waist measurements are taken midway between the lowest rib and iliac crest. The measurement should be taken while standing erect and breathing normally.
- Dyslipidemia – This refers to abnormally low amounts of HDL (good) cholesterol and high LDL (bad) cholesterol.
- Insulin resistance – This is when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, causing high blood sugar levels.
What are the various Risk factors of metabolic syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is a cluster of risk factors that increase your chances of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. These diseases are all associated with serious health complications. The main risk factors for MS are obesity, high blood pressure (>140/90 mm Hg), abnormal cholesterol levels (<200 mg/dL for men or <130 mg/dL for women), and elevated triglycerides (>150 mg/dL).

In addition to these common risks, people who have MS often have other unhealthy habits like smoking and drinking too much alcohol. Obesity is the single most important risk factor for developing MS, nearly two-thirds of people with the condition are overweight or obese.
Having a history of heart disease, Having type 2 diabetes Having a family history of diabetes, or How do reduce the risks associated with developing metabolic syndrome? There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, but here are some tips to reduce the risks associated with developing metabolic syndrome: Eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat foods. Exercise regularly. Avoid smoking. Know your blood pressure and cholesterol levels and take action if they are high or if you have any risk factors for heart disease or stroke.
How do I prevent or reverse metabolic syndrome?
- Don’t eat sugar/carbs: Sugar and carbs are two of the biggest culprits here. Sugar causes insulin spikes and those cause inflammation. We should only ingest sugars from natural sources like fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, grains, etc… Anything else is just pure junk. Carbs are even worse. They turn into sugar fast and then spike our blood sugar levels. The result is inflammation and health problems.
- Get rid of refined foods: Refined foods are what make us fat and sick. Refined grains, processed meats, fried foods, fast foods, soft drinks, sugary sweets, unhealthy fats, etc. All this stuff makes our bodies work overtime to try and regulate our blood sugar and we store it as body fat.
- Don’t drink alcohol: Alcohol is a toxin. It lowers your inhibitions, makes you stupid, and generally destroys your life. Alcohol doesn’t give you energy. It gives you a hangover.
- Eat healthy fats: Healthy fats help lower cholesterol, boost energy, reduce cravings, and increase brain function. Omega 3 fatty acids are great too. Most Americans are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids.
What are the complications of Metabolic syndrome?
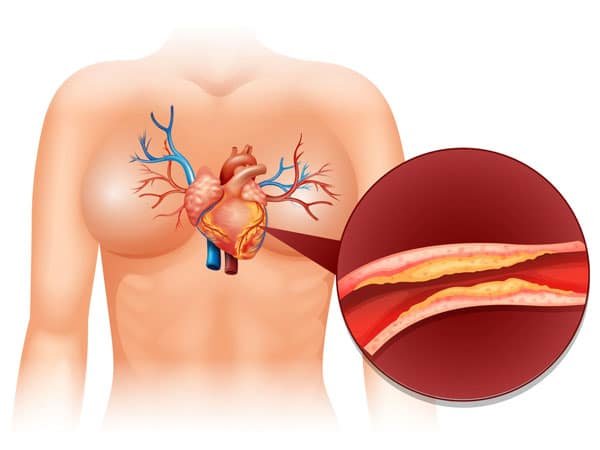
There is an increasing awareness about metabolic syndrome among people all over the world. MS has become one of the most common conditions affecting adults in industrialized countries. Although there are many different causes of MS, its major complication is atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries due to increased fat accumulation throughout the body.
The most important aspect of metabolic syndrome is the presence of at least three of the following: obesity, elevated blood pressure, impaired fasting blood sugar, elevated blood triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol. Associated complications of metabolic syndrome include decreased exercise capacity, increased insulin resistance, abnormal glucose tolerance, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and elevated blood levels of inflammatory markers.
Does Metabolic syndrome cause Diabetes?
Metabolic Syndrome happens due to abnormal levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, and obesity. Diabetes is the result of prolonged exposure to high glucose levels. Both conditions are related to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance leads to hyperinsulinemia which causes changes in fat cells resulting in excess body weight. This excess weight increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. To control diabetes one can choose various treatments that include insulin pump therapy, medications, and insulin injections. Insulin pump therapy is gaining a lot of attention as it is quite easy and comfortable to use. Do check out INSUL by AgVa, which is quite affordable and helps in managing blood sugar levels.