Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. The symptoms are similar to other types of diabetes. Gestational diabetes leads to high blood sugar that can affect both mother and child. The good news is blood sugar of mothers with gestational diabetes gets to normal levels after delivery, though there will be a need for regular checking of blood glucose levels to get rid of this permanently.
Also, adopting a good lifestyle like exercising regularly, eating healthy food will slowly lower the symptoms of gestational diabetes. On the other hand, if not managed early, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. The symptoms of gestational diabetes are not noticeable in starting, still expected mothers should know its symptoms.
Symptoms

In most cases, no severe symptoms appear. Increased thirst and frequent urination can be felt by pregnant women.
Causes
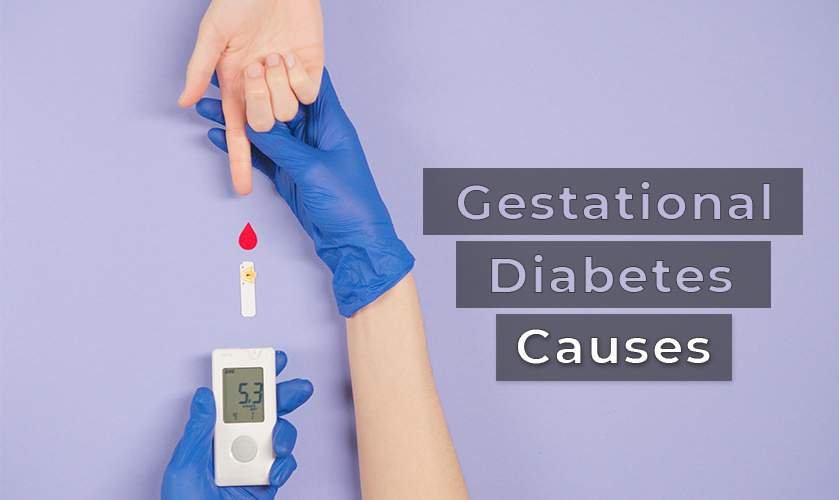
Till now, it is not clear why gestational diabetes occurs in some women and not in others during pregnancy. But obesity before pregnancy has a big role in developing the condition. Also, the hormonal changes during pregnancy affect the blood glucose levels and may cause gestational diabetes and can raise blood sugar levels.
Risk factors

Some women are highly vulnerable to developing gestational diabetes due to:
- Excessive weight
- Inactive lifestyle
- History of diabetes or prediabetes
- Previously delivering baby more than 9 pounds or 4.1kg
- Some race of women such as Hispanic, American Indian, etc are at high risk of developing prediabetes
How does it affect your baby?
Heavyweight at birth: a mother having high blood sugar than normal may have an overweight baby- about 9 pounds or more.
Premature birth: high blood sugar increases the risk of premature birth due to the heavy weight of the child. Or maybe an early delivery is recommended.
Difficulty in breathing: infants born from mothers having gestational diabetes may experience breathing disorders like respiratory distress syndrome. It is a condition that makes breathing difficult in infants.
Hypoglycemia: in some cases, babies born with gestational diabetes have low blood sugar just after birth for a short time. If it is serious, can even cause seizures in the baby. Timely feeding and an intravenous glucose solution can normalise the blood sugar level again.
Risk of developing type 2 diabetes in later life: babies of mothers having gestational diabetes have a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and obesity in later life.
Stillbirth: unmanaged gestational diabetes can cause either baby’s death before or shortly after birth.
Risk factors for mothers
Hypertension: Gestational diabetes increases the risk of high blood pressure.
Preeclampsia: It is a severe complication in pregnancy that causes high blood pressure and put the lives of both mother and baby at risk.
Surgical delivery: Mothers having gestational diabetes often undergo a C-section delivery.
Diabetes in later life: Mothers having gestational diabetes have high chances of developing type 2 diabetes in future.
Prevention

Prevention tips don’t guarantee to prevent gestational diabetes. But adopting more healthy habits will eventually prevent the condition. Thus, if women want to prevent themselves from further diabetes in future, they should follow the given tips:
Eat healthy foods: take foods high in fibre and low in fats and calories. Rather consume more fruits and vegetables.
Be active: adopting a healthy lifestyle and regular workouts during and after pregnancy help people to avoid gestational diabetes. A 30-minute workout is enough every day. Also, people should try to take short walks in a whole day routine.
Start pregnancy with a healthy weight: when planning for a baby, women should manage their weight before getting pregnant.